About Stroke
Stroke is the No. 5 cause of death and a leading cause of disability in the United States.

Stroke is a disease that affects the arteries leading to and within the brain. It is the No. 5 cause of death and a leading cause of disability in the United States.
A stroke occurs when a blood vessel that carries oxygen and nutrients to the brain is either blocked by a clot or bursts (or ruptures). When that happens, part of the brain cannot get the blood (and oxygen) it needs, so it and brain cells die.
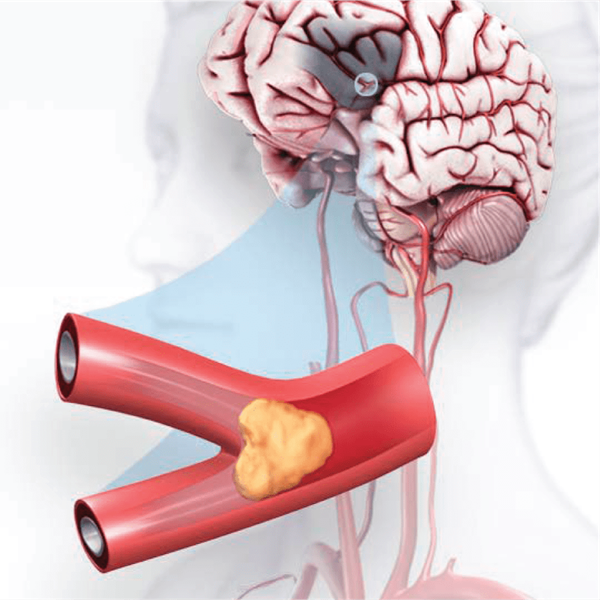
What are the types of stroke?
Stroke can be caused either by a clot obstructing the flow of blood to the brain (called an ischemic stroke) or by a blood vessel rupturing and preventing blood flow to the brain (called a hemorrhagic stroke). A TIA (transient ischemic attack), or "mini stroke", is caused by a temporary clot.
What are the effects of stroke?
The brain is an extremely complex organ that controls various body functions. If a stroke occurs and blood flow can't reach the region that controls a particular body function, that part of the body won't work as it should.


Stroke Hero Toolkit
A simple guide for educators, mentors, advocates, youth leaders and parents.
Explaining Stroke
Many people think a stroke happens in the heart, but it happens in the brain. Our Explaining Stroke booklet explains how a stroke happens, different types of stroke and how to prevent a stroke.
Ways to Prevent a Second Stroke
About one in four stroke survivors suffers a second stroke. There are steps you can take to reduce your risk by working with your health care professional and developing a prevention plan.
TIA and Stroke: Medical Emergencies
When someone has shown symptoms of a stroke or a TIA (transient ischemic attack), they require immediate medical attention. A doctor will gather information and make a diagnosis and begin a course of treatment depending on the cause of the stroke.
